Directory : Find All Locations in Saudi Arabia
Advertisement
Browse by Keyword, City or Neighborhood
Locations recently added
Address 9CW6+32G – 9CW6+34H، – Tamrah 18634، – Saudi Arabia
Address Prince Mutaib bin Abdulaziz Rd – Al-Rehab – Jeddah 23344 – Saudi Arabia
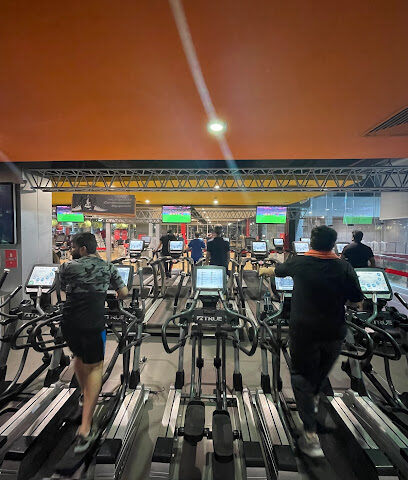
Categories Gym – Jeddah Gym – Saudi Arabia Jeddah
Address 5268، الصمد، رابغ 25728 – Saudi Arabia – –
Address King Abdul aziz Street , building number 5461 Cornish Road , Beside Alhob Market – Dammam – Saudi Arabia –
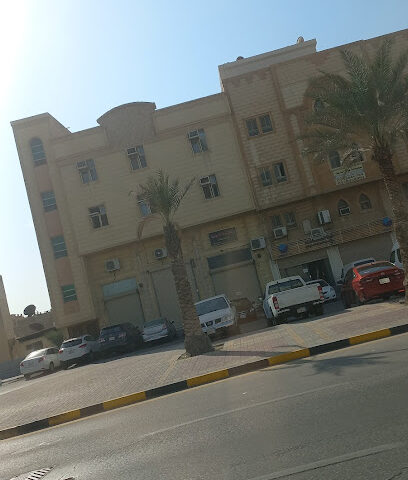
Categories Dammam Hotel – Dammam Hotel – Saudi Arabia
Address 5301 Istanbul St, Al Mishal, Riyadh 14325 7913 Prince Mohammed Bin Abdulrahman Bin Abdulaziz – 7913, Al Mashael – Riyadh 14327 – Saudi Arabia
Address 7CC5+6R4 – اسامة بن زيد – Almantiqah Almarkaziyyah – Taif 26522, Saudi Arabia
Register your office in our database
You can customize your page with text and images to make it stand out in your area.